Cloud computing has become the foundation of the modern business. Whether it is storing customer data or running business-critical applications, companies of all sizes use the cloud day in and day out. However, the risks increase with the adoption. Cybercriminals are always on the prowl to find a loophole in a poor security implementation, misconfiguration, or user laxity.
In reality, it has been reported recently that misconfigured cloud services are among the greatest causes of data breaches globally. To businesses, one breach could spell loss of revenue, legal problems, and reputation damage in the long term.
The positive news? The majority of these risks are preventable or can be minimized with the use of practical cloud security tips. In this guide, I will show you effective measures that you can deploy to ensure your cloud environments are secure and resistant to attacks.
What is Cloud Security?

Cloud security is a term that is applied to the practices, technologies, and policies that are applied to protect data, applications, and services that are implemented on the cloud. Unlike the time when only in-house servers were used, businesses now store massive amounts of sensitive data on the clouds of such companies as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
Moving to the cloud does not mean that security is automatically handled. It is also the responsibility of cloud providers to make sure their infrastructure is secure, although you should still take care of data, access controls, and configurations.
You must think of it as a rented apartment: locks and security cameras will be installed by the owner of the building, but it is your duty to lock your door and keep your valuables locked. Cloud security is not an exception; it is a shared responsibility between the provider and you.
Why Cloud Security Matters More Than Ever
The transition to the cloud-based systems has transformed the way business is being done. Regardless of the size of the company, every organization relies on the cloud to store data, execute programs, and work with teams.
But there are risks that come with this convenience. The highest price to date is the average cost of a breach to a company of $4.45 million, which is the highest price in the Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 by IBM. The most prevalent reasons of those breaches remain to be misconfiguration of the cloud.
This implies that cloud security is not only an IT concern, it is a survival concern of the business. Without the protection of your systems, your business will be exposed to:
- Data theft destroys customer trust.
- Ransomware attacks that are to be paid high prices.
- Penalties for failure to adhere to security laws.
- Operation halt that halts productivity.
Most of these risks can be avoided with the right strategies in place. Common sense cloud security advice comes in handy there.
Practical Cloud Security Tips
Strong cloud security isn’t achieved by a single tool or rule; it’s about building multiple layers of defense. Below are 10 detailed tips that companies (from startups to enterprises) can follow to reduce risks and safeguard sensitive data.
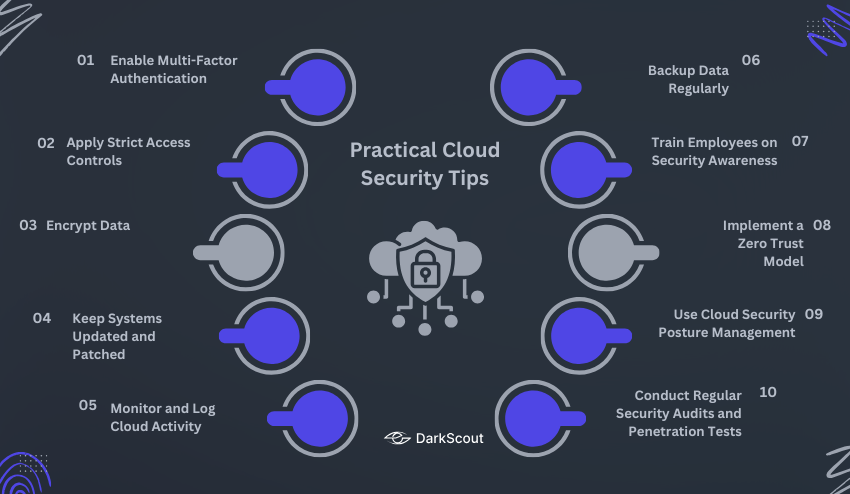
1. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords are not sufficient on their own since they are easy targets. They can be stolen by attackers during phishing or using brute-force tools, or can be purchased on the dark web. MFA provides an additional layer of security as a second form of verification is needed, e.g., a text message, authenticator app, biometric scan, or a hardware key.
The reason it is important: Even with a password in hand, a hacker will not be able to log in without the second factor. This reduces successful account takeovers to a very minimal number.
How to implement:
- Enforce MFA on all accounts and not just admins.
- Use authenticator applications (Google Authenticator, Authy) where possible (since SIM swaps are a threat).
- Train workers that they should never accept unexpected MFA requests.
Example: In the year 2022, when Uber was severely breached due to an attacker spamming MFA requests until one employee accepted it. The lesson? MFA is effective only when the users know how to react to the suspicious prompts.
2. Apply Strict Access Controls (Least Privilege Principle)
Not all employees should have access to all the files. Granting everyone extensive privileges will give a single compromised account access to the entire system. Instead, restrict access on the basis of roles and responsibilities.
Why it matters: Access is limited, which minimises the harm caused by an insider who turns rogue or an attacker who gains access to an account.
How to implement:
- Apply Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to restrict access by job role.
- Review and update access rights on a regular basis.
- Immediately, if an employee leaves the company, accounts are removed.
Example: A hospital only allowed the treating doctors to access the patient records. Attacks on internal staff accounts were also averted due to the segmentation of access to other sensitive files.
3. Encrypt Data (In Transit and At Rest)
Encryption encrypts your data in a form unreadable to everyone unless you have the correct decryption key. This is to make stolen or intercepted data unusable by the attackers.
Why it matters: Encryption prevents attackers who gain access to your systems to simply copying and sell plain text files.
How to implement:
- Use TLS (Transport Layer Security) in all transfers.
- Encrypt files with AES-256.
- Take care of encryption keys – keep them in a secure key management service (KMS).
Example: Dropbox also encrypts data at rest with AES-256 and encrypts data in transit with SSL/TLS. Even in case data packets were intercepted, they would be unreadable.
4. Keep Systems Updated and Patched
Hackers always scan the software that has known vulnerabilities. Failure to patch in a timely fashion leaves the door open.
Why it matters: A lot of high-profile breaches occurred because organizations failed to update.
How to implement:
- Turn on automatic updates of operating systems, applications, and cloud services.
- Apply centralized patch management to big organizations.
- Vulnerability scans are done to identify unpatched software.
Example: The 2017 Equifax breach (exposing 140M+ people) was due to a single Apache Struts vulnerability that had not been patched. It would have been prevented by an update in time.
5. Monitor and Log Cloud Activity
Logging is provided by cloud providers that record user activity, changes to the system, and network traffic. You will not realize a breach until it is too late without monitoring.
The importance: Real-time monitoring will be able to detect intrusions before the attackers go further into your system.
How to implement:
- Activate cloud logging services (AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, Google Cloud Logging).
- Install alerts on suspicious activity (failed logins, unusual downloads of information).
- Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) to aggregate logs.
- Many organizations also rely on MDR security to continuously monitor cloud activity and rapidly respond to confirmed threats.
An example: A financial institution was able to detect a breach early because its system was flagging repeated logins to an unusual IP address. Due to swift detection, sensitive data was not stolen.
6. Backup Data Regularly
Cloud services are not resistant to outages, ransomware, or accidental deletion. A safe, standalone backup will make recovery possible with speed.
Why it matters: The final layer of protection against ransomware is backups. You can restore your data without paying in case it is encrypted by attackers.
How to implement:
- Use the 3-2-1 rule: 3 copies, 2 types of storage, 1 off-site
- Automate back up on a daily or weekly basis
- Recovery of tests is regularly performed to make sure that backups are functional.
Example: In the case of the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, the company lost millions as operations were disrupted. Verified backup companies will be able to recover at a much faster rate without having to pay a ransom.
7. Train Employees on Security Awareness
Technology is no good without teams that are knowledgeable of how to use it safely. Most cloud breaches are the result of human error such as falling prey to phishing emails.
Why it matters: One careless click is all it takes to break even the toughest firewall.
How to implement:
- Perform phishing simulation tests on a regular basis.
- Train personnel on good passwords and secure sharing of data.
- Include security training as a part of onboarding.
Example: Google conducts phishing simulations on its employees on a regular basis. This effectively minimized successful phishing attacks in the long run.
8. Implement a Zero Trust Model
Zero Trust is about never automatically trusting anybody, whether inside or outside the network. Rather, each request is to be validated prior to granting access.
Why it matters: Insider threats and lateral movement (attackers moving through systems after one breach) are reduced.
How to implement:
- Install continuous authentication (repeatedly verify the identity of the user and/or the device).
- Micro-segment networks to segregate workloads.
- Enact stringent authentication of each request.
Example: Microsoft has implemented a Zero Trust model on all internal systems, including requiring re-authentication of internal users. This tactic assisted in preventing lateral movement in an attempt of breach.
9. Use Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools
One of the leading causes of breaches in the cloud is misconfigurations. A CSPM tool is a tool that automatically checks your environment for risky configurations.
Why it matters: A single error (such as leaving a cloud storage bucket open) can put millions of records at risk.
How to implement:
- Implement CSPM tools such as Prisma Cloud, Wiz, or Orca Security.
- Automate notifications of settings that are not in compliance.
- Integrate with DevOps to identify problems early.
Example: In 2019, Capital One experienced a huge breach due to an incorrectly set AWS bucket. A CSPM tool would have alerted to the misconfiguration prior to exploitation.
10. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Tests
Security is not a set-and-forget. Testing on a regular basis can assist in identifying blind spots before they are exploited by attackers.
Why it matters: Cloud environments are dynamic – audits are necessary to identify any unseen vulnerabilities.
How to implement:
- Carry out an internal security audit once every quarter.
- Engage with third-party penetration testers on an annual basis.
- Compare to the standards such as ISO 27001, SOC 2, or NIST.
Example: It is not uncommon to find many corporations in the Fortune 500 that conduct regular red teaming exercises, in which ethical hackers emulate actual attacks. These tests tend to unearth gaps that were not identified by internal teams.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Security Tools
Selecting the right tools is essential in enhancing your cloud security. There is a wide range of solutions available in the market but not all solutions are equally good. The choice of the appropriate ones is based on the size of your business, cloud environment, and risk tolerance.
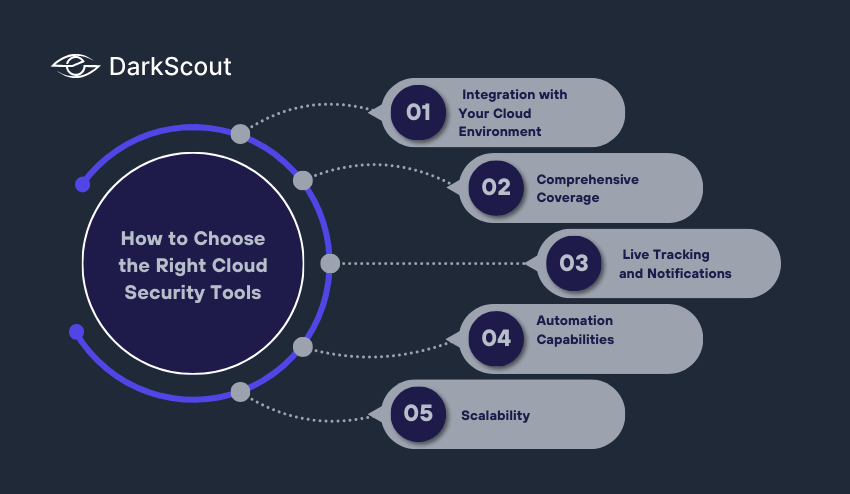
1. Integration with Your Cloud Environment
Ensure that the tool is compatible with your current cloud systems (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud). Inadequate integration may leave holes in protection.
2. Comprehensive Coverage
Seek tools that address identity and access management, threat detection, encryption, and compliance reporting. A multi-layered tool simplifies the work.
3. Automation Capabilities
Automation can assist in the identification of threats, patching and alert management without the need of constant human supervision. It enhances productivity and lowers man-made mistakes.
4. Live Tracking and Notifications
Identification of suspicious activity at an early stage can help to stop breaches before they get worse. Select tools that have actionable, real-time alerts.
5. Scalability
Your security tools must expand as your business does. Scalable solutions will enable you to ensure that your coverage is not compromised when cloud usage and staff numbers increase.
Types of Cloud Security Tools
- Firewalls and Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Protect against external attacks.
- End Point Security: Secures devices that connect to the cloud.
- Access and Identity Management (IAM) Tools: Manage users and authorizations.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Discover configuration and compliance vulnerabilities.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collects all the logs and alerts in order to accelerate response to incidents.
Conclusion
Cloud security is not a luxury anymore it is mandatory. Breach may be expensive, reputation may be destroyed, and operations may be disrupted. Strong identity and access management, multi-factor authentication, encryption, regular updates, and monitoring of activities can help businesses to protect sensitive data. Security is further reinforced by backups, training of the staff, a Zero Trust approach, CSPM, and regular audits.
Good cloud security is based on multi-layered security and continuous monitoring. Security is an ongoing activity and by means of such practices, organizations can protect data, retain customer trust and grow comfortably in the cloud.