Big businesses are no longer the only ones affected by cyber threats. Any organization that goes online is vulnerable to phishing attacks, malicious websites and malware. The old-fashioned firewalls and antivirus applications, which are aimed at securing the network boundary are no longer sufficient in the current cloud-first and remote working conditions.
This is where a Secure Web Gateway (SWG) is required.
The secure web gateway serves as a shield between the users and the internet. It monitors web traffic instantly, blocks suspicious sites, filters unsafe content, and blocks threats before they get into internal systems. SWGs are also able to offer protection to users regardless of their location, be it in the office, at home, or when they are using cloud applications unlike legacy security tools.
What Is a Secure Web Gateway?
SWG is a security tool that implements security measures on web traffic. It tracks user requests, file downloads, and web sessions to prevent malware, phishing, and data leakage.
Should a user attempt to browse a malicious site, download an infected file or upload important company information to an unverified location, the SWG will automatically prevent the activity. This web-based protection is particularly useful when remote workforces and SaaS-based workflows are present in an organization because traffic is frequently not going through the traditional network.
The contemporary secure web gateways integrate various functions into one platform such as URL filtering, malware protection, application control, and data loss prevention (DLP). This provides the IT teams with better visibility and control on the usage of the internet within the organization.
SWGs are now part of the contemporary cybersecurity measures. They are a fundamental component of zero-trust architectures and SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) systems, which means that they will be required by businesses of all sizes in 2026.
The Importance of a Secure Web Gateway in Businesses
There has been a drastic change in the manner in which businesses are conducted. Workers are no longer behind one office firewall. Rather, they are home workers who use public Wi-Fi and are dependent on cloud applications. On the one hand, this flexibility enhances productivity, but on the other hand, it creates innumerable points of entry to cybercriminals. A secure web gateway is meant to overcome these challenges.
Key reasons businesses adopt SWG solutions include:
- Web-based threat protection– Malware, ransomware, phishing sites, and malicious downloads are ubiquitous. A web gateway is used to check traffic on a real-time basis and filter out harmful content before it reaches the users.
- Information security and privacy– In lots of sectors, there are stringent policies that pertain to the management of sensitive information. Such features as data loss prevention (DLP) and policy enforcement can assist organizations to remain compliant.
- Enhanced employee productivity– SWGs minimize distractions and dangerous downloads and do not compromise on security.
- Zero trust and SASE models support – SWGs continuously verify all user activity, and therefore are a critical component of modern network architecture.
- Remote and cloud work, which is safe – SWGs protect remote employees, working across cloud applications, mobile devices, and home networks.
With threat protection, compliance support, and productivity controls in place, a secure web gateway is no longer a luxury item, but it is a necessity in a modern business organization.
Key Features of a Secure Web Gateway
A web gateway is not simply a web filter. It integrates various layers of security technologies in a single solution. The following are the main characteristics that render SWG solutions successful:
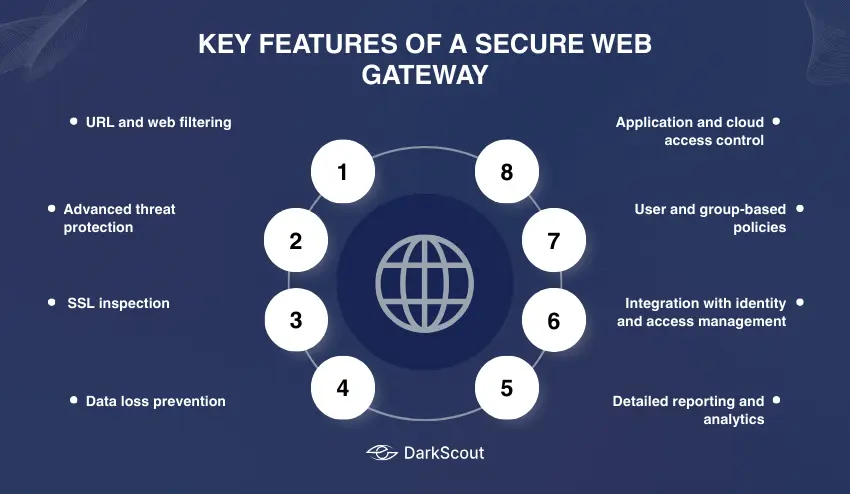
1. URL and web filtering
Blocks access to malicious or inappropriate websites by comparing the URLs and domains to the current threat intelligence databases.
2. Advanced threat protection
It is based on the techniques of sandboxing, antivirus scanning, and signature detection to prevent malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks.
3. SSL inspection
Decrypts and inspects encrypted web traffic (HTTPS) to identify any hidden threats without compromising privacy or compliance standards.
4. Data loss prevention (DLP)
Helps in preventing sensitive data, e.g., financial records or customer data, from being leaked outside the organization.
5. Application and cloud access control
The access to SaaS applications is checked and controlled by SWG, and it also provides secure usage of apps such as Google Workspace, Dropbox, or Microsoft 365.
6. User and group-based policies
Enables IT admins to develop their own security policies based on roles, departments, or types of devices.
7. Integration with identity and access management (IAM)
Cooperation with identity providers (IdPs) to implement zero trust policies and authenticate users in real-time.
8. Detailed reporting and analytics
Gives visibility of network traffic, user behavior and threat activity to enhance the management of network security.
Combined, these characteristics render secure web gateways a major component of a cloud security and zero-trust network access approach. These capabilities are particularly advantageous to businesses that operate remotely and in hybrid environments.
Secure Web Gateway vs. Firewall vs. Proxy
Most organizations mix up secure web gateways with the old fashioned firewalls or proxy servers. Although each of the three is a security tool, they are used to serve different purposes in securing web traffic and corporate data. The differences also enable IT teams to implement the appropriate solution to their environment.
| Feature | Secure Web Gateway (SWG) | Firewall | Proxy Server |
| Primary Function | Monitors, filters, and protects web traffic | Controls network traffic based on ports, protocols, and IPs | Intermediary for requests between client and web server |
| Focus Area | Web security, malware protection, data loss prevention | Network-level security | Request forwarding, caching, limited content filtering |
| Deployment | On-premises, cloud, hybrid | On-premises or cloud | On-premises or cloud |
| Threat Protection | URL filtering, malware scanning, SSL inspection | Basic intrusion prevention | Limited; can block specific sites or content types |
| Use Case | Protect users accessing internet & cloud apps | Block unauthorized network access | Manage and cache web traffic for efficiency |
| Integration | Works with SASE, CASB, DLP | Often integrates with SWG or IDS/IPS | Sometimes integrates with SWG for filtering |
Summary
- Firewalls are network-based and filter traffic at the port and protocol but are not able to filter web content in depth.
- Proxy servers are intermediaries that are used to redirect requests and can provide simple filtering, but do not provide full threat protection and DLP.
- Secure web gateways are designed to offer specific web protection, monitoring, and enforcement of policies, and they are best suited to the contemporary businesses that have cloud applications, remote users, and emphasize on zero trust security.
These tools are frequently stacked together in order to choose the appropriate solution. SWGs are used in conjunction with firewalls and proxies in many organizations in an effort to have a comprehensive security posture.
Types of Secure Web Gateway Solutions
Secure web gateways are offered in various deployment models with their own benefits depending on the need of the business. The knowledge of these types assists organizations in selecting the appropriate solution to their security strategy.
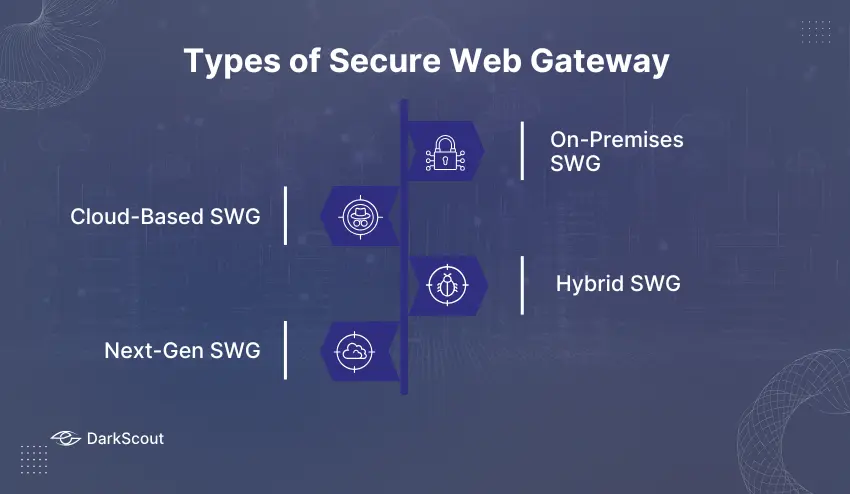
1. On-Premises SWG
Secure web gateways are installed on-premises and are directly installed on the network of the company. They provide complete configuration, policy and update control to the IT teams.
- Advantages: Full control, minimal latency, does not need the internet.
- Cons: It is expensive to install, needs maintenance and less flexible to remote users.
2. Cloud-Based SWG
Cloud SWGs are internet based and cover the user irrespective of the location. They can be combined with other cloud security solutions and SASE systems.
- Advantages: Easy scalability, remote work, low infrastructure requirements.
- Cons: It may have a latency, it will rely on internet connectivity, it will require subscription.
3. Hybrid SWG
Combines on-premises and cloud deployment options allowing for consistent and flexible protection. The on-premises devices can funnel critical traffic, while cloud SWG can manage all other exchanges for remote users and applications that access cloud services.
- Benefits: More flexibility, more balanced control, more complex networks.
- Drawbacks: Can be difficult to control, must be able to enforce policies consistently.
4. Next-Gen SWG
These solutions use AI and machine learning for advanced threat detection, integrate with CASB and endpoint security, and support a zero-trust model.
- Pros: Advanced threat detection, predictive analytics, and cloud integration.
- Cons: Higher cost, could be pricey, and will necessitate advanced IT knowledge.
The choice of which kind of secure web gateway will depend on the location of your workforce, budget, complexity of the network, and the degree of cloud integration required. Cloud-based SWGs are increasing in popularity with the advent of remote working and SaaS applications. On-premises solutions can and still make sense when there is an organization serving compliance/ regulatory needs.
Top Benefits of a Secure Web Gateway
Secure web gateway has a number of advantages to both the small and large businesses. SWGs are a vital component of the existing IT security measures as they may be applied to improve compliance and productivity, and cybersecurity.
- Better Web Protection – SWGs block websites with malicious intent, prevent phishing and malware before they get in the hands of the user and provides real-time protection against threats on all devices.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)– They make sure that the sensitive company data is not leaked out either accidentally or intentionally. This is necessary in the industries where compliance levels are high like the finance, healthcare and legal industries.
- Remote Work and Cloud Apps Support – SWGs can support the principles of zero trust security by providing secure access to cloud-based applications regardless of where the worker is located as more workers work remotely and use cloud-based applications.
- Improved Productivity – SWGs give employees the ability to be focused and at the same time they are able to collaborate and use the web safely as they used to by blocking access to sites that contain risky or non-work related information.
- Regulatory Compliance – The majority of SWG solutions allow reporting and auditing functions to help companies meet industry standards, including GDPR, HIPAA and PCI DSS.
- Scalability – Cloud-based SWGs can be scaled up or down accordingly as an enterprise grows or adopts new SaaS applications, which is why they are appropriate to dynamic companies.
- Visibility and Analytics – SWGs provide insights into user behavior, network traffic, and threat trends, which allow IT teams to actively adjust policies and respond to incidents faster.
When these benefits are combined, secure web gateways are not only capable of protecting against cyber threats, but also enable successful business processes and regulatory adherence.
Challenges & Limitations of Secure Web Gateways
Although secure web gateways are very protective to the businesses, they are not without their challenges. The awareness of these limitations aids the organizations in planning the deployments better.
- Cost of Implementation – Premium SWG implementations particularly cloud-based or next-generation implementation are not cheap. The organizations are to take into account the subscription fee, licensing, and the cost of possible hardware. Note: ROI can be assessed by comparing the avoided cost of breaches with the cost of the SWG investment.
- Complex Policy Management – Establishing elaborate filtering policies, user access policies, and compliance policies may be tricky. Hint: Begin with general policies and tailor them according to department or position.
- Performance and Latency Concerns – Sometimes decryption of encrypted traffic (SSL/TLS) slows down internet access or application performance. Hint: To achieve low latency, traffic routing should be optimized, and high-risk traffic should be selectively inspected.
- Poor Mobile or Remote Support in Certain Deployments – On-premises SWGs might not be able to cover remote users completely. Hint: Cloud-based or hybrid SWG solutions may be considered to make sure that all devices are covered by the protection.
- Reliance on Continuous Updates – The data on threat intelligence, malware signatures, and policy rules should happen regularly. Note: Turn on auto updates, or select vendors that have real-time threat feeds.
In spite of these, a secure web gateway can operate effectively if there is thoughtful management, vendor selection, and continuous management in order to mitigate its negative aspects.
How to Choose the Right Secure Web Gateway

A secure web gateway is very important in achieving high levels of web security, compliance, and productivity. Various vendors and types of deployment models are available and IT teams require a systematic way of making the right decision.
- Evaluate the Needs of Your Organization- Begin by determining network traffic, the size of remote workforce, the use of cloud applications, and compliance needs. This assists in deciding on the best on-premises, cloud or hybrid SWG.
- Check Core Security Features – Find the necessary features such as URL filtering, malware protection, inspection of the SSL, data loss prevention (DLP) and application control. These attributes guarantee all-round security to web traffic and cloud applications.
- Assess Integration Possibilities – make sure that the SWG is integrated with other security tools, including firewalls, SIEM platforms, CASB, and identity management solutions. This is particularly critical to those organizations that are implementing zero-trust security or SASE.
- Consider Performance and Scalability – Test the ability of the solution to support your user base without affecting performance. Cloud based SWGs are normally simpler to scale with an increased workforce or with new applications of SaaS.
- Check Vendor Reputation and Support- Check the reliability of vendors, how often they are updated, customer support, and industry reviews. Find those that have a high threat intelligence level and a history of securing other businesses like yours.
- Budget and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)- Consider subscription costs, licensing, training, and potential hardware or maintenance costs. Economical use of costs versus security benefit.
- Pilot Testing – Considering this, a pilot or trial run should be done to determine the performance of the SWG in your environment. Pre-deploy threat detection, policy enforcement, and user impact.
These steps can ensure that businesses can choose a secure web gateway that fits their security strategy, regulatory requirements, and IT infrastructure with a great deal of confidence.
Future of Secure Web Gateways
The field of cybersecurity is rapidly evolving and secure web gateways (SWGs) are evolving accordingly. SWGs are smarter, faster, and more manageable with more employees working remotely and using cloud applications.
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is one of the trends. Through these technologies, SWGs are able to identify new threats, learn the patterns of web traffic and automatically modify rules to block attacks before they occur. This assists businesses to be ahead of hackers.
The other significant change is the emergence of SASE (Secure Access Service Edge). SASE integrates SWG with cloud networks and zero trust. This implies that the users can access the internet and cloud applications without any security concerns, as well as the IT teams are still in control.
Zero-trust security is also altering the operation of SWGs. SWGs continuously scan users, devices, and risk levels instead of assuming that all people inside the network are safe. This provides security to both employees, laptops and cloud tools at any given time.
Lastly, SWGs are increasingly becoming more integrated with other security solutions such as CASB, endpoint protection, and threat intelligence feeds. This enables the businesses to better see threats, respond to them more quickly, and comply with rules more easily.
Concisely, the future of secure web gateways is smarter, cloud-enabled, zero-trust enabled, and completely integrated with other security systems. Companies that embrace such solutions will remain secure in the dynamic cyber environment.
Conclusion
Secure web gateway is no longer optional. It is an essential condition of securing the users against malware, phishing, and unsafe websites and aiding in data loss prevention and compliance. With remote work and cloud applications becoming the norm, SWGs will guarantee that employees are able to access the web and business resources at any place, or time, securely.
The selection of the appropriate SWG is based on organizational requirements, deployment options, scalability and security features. The use of SWG solutions in the cloud is on the rise, and they are flexible to serve modern, hybrid, and on-prem environments.
Moving forward, secure web gateways are going to be more compatible with AI-based threat detection, zero trust security frameworks, and SASE. Investing in an SWG now enhances the long-term security, enhances the performance of operations, and provides a secure digital environment to ensure long-term productivity.