Cyber threats are evolving with each passing day, and the old security tools are not keeping pace. Ransomware, phishing, and advanced persistent threats are threats that affect organizations of every size. Firewalls or antivirus software are no longer sufficient in this setting.
This is where MDR Security comes in. Managed Detection and Response services are a combination of both high-technology and human intelligence to actively monitor, detect, and respond to threats on the fly. MDR offers a holistic solution, whether you are an SMB trying to protect your growing network or a large enterprise trying to minimize dwell time on incidents.
This guide will address all that you need to know about MDR Security such as what it is, why it is necessary, how to effectively implement it in your organization and what best practices should be adopted by both small and large organizations.
What is MDR Security?
Managed Detection and Response (MDR Security) is an active cybersecurity service used to assist organizations in detecting, investigating, and responding to threats before they become critical. MDR integrates both high-tech and human resources to constantly monitor and defend digital environments unlike traditional security tools.
It offers 24/7 Threat Monitoring on endpoints, networks and cloud-based systems, so even advanced attacks such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) can be identified and resolved within a short time.
In its simplest form, MDR is about Managed Detection and Response Services that do not simply alert organizations about threats, but actively search for risks, scan suspicious behavior, and counteract incidents as they happen.
MDR focuses on proactive protection, unlike the traditional Managed Security Services (MSS) which focuses on passive defense, combining automated solutions with professional analysts to minimize dwell time and enhance response time.
MDR Security provides protection to any size organization, and it does not need a full in-house security team to provide scalable protection to its clients, which makes it a viable solution to enhancing cybersecurity effectively.
Core Components of MDR Security
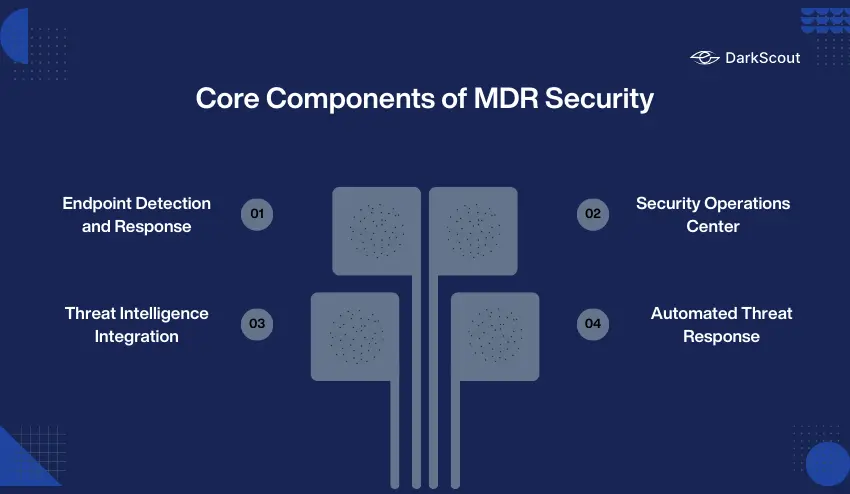
1. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):
EDR scans all the endpoints, such as laptops, servers, and mobile devices, to detect suspicious activity or anomalies. It gives a profound insight into the activity of the system and can promptly detect malware, ransomware, or intrusion attempts. The EDR can prevent breaches by analyzing endpoint data continuously to prevent the spread of breaches within the network.
2. Security Operations Center (SOC):
The SOC is the core point where security analysts track, investigate, and act on threats. Analysts examine alerts, conduct threat hunting, and organize incident response. A properly staffed SOC will guarantee that any potential risks will be mitigated in real-time, to minimize dwell time and impact to business operations.
3. Threat Intelligence Integration:
MDR services use both internal and external threat intelligence to help them stay ahead of new attack patterns. This integration enables organizations to foresee threats, detect signs of compromise, and enhance accuracy in detection. It also assists the security teams to gain knowledge of attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
4. Automated Threat Response:
MDR systems can contain and mitigate threats within seconds using automated workflows, and in many cases, before human intervention is required. This involves isolating infected machines, blocking rogue IP addresses, or closing hacked accounts. Automation saves on time to respond, minimizes harm, and enables analysts to concentrate on more sophisticated threats.
MDR vs Traditional Security
Conventional security measures are largely reactive and depend on firewall, antivirus software or network logs alerts. These tools are able to identify the obvious threats, but in most cases, they are not able to detect advanced or hidden attacks in real-time.
MDR Security, however, is a blend of Proactive Threat Hunting and human intelligence, and sophisticated analytics. It does not sit back and wait to be alerted, but it proactively scans endpoints, networks, and cloud environments looking for anomalies, suspicious activity, and possible breaches.
Connection to tools such as SIEM will help to contextualize all alerts, and incident analysis will be quicker and more precise. This enables organizations to act swiftly and efficiently and reduce damage and downtime.
MDR offers a multi-layered approach to defense, which evolves based on the changes in the threat, such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), ransomware, and insider attacks. MDR assists organizations to have a more robust and resilient cybersecurity posture by decreasing dwell time and increasing the speed of response.
Why Organizations Require MDR Security
The nature and frequency of cyber threats are becoming increasingly complex, and the traditional security solutions are no longer enough. To reduce the damage, organizations require a system that is capable of identifying and responding to threats in real-time.
MDR Security offers 24/7 Threat Monitoring and Proactive Threat Hunting, which ensures that potential risks are detected and mitigated before they grow out of control. It also assists organizations to remain within the industry regulations and liberate the internal IT to concentrate on the core business operations.
In the case of SMBs, MDR is a scalable and affordable service that does not need a fully manned in-house Security Operations Center (SOC). In large organizations, it will improve the existing security infrastructure and dwell time of critical threats, such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
Through MDR, organizations can improve their cybersecurity stance, secure sensitive information, and survive even advanced attacks.
Types of Detection and Response Solution
When we talk about MDR Security, one should know the various detection and response solutions. The types are each purposeful and may be combined according to the security requirements of an organization.

1. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):
Monitor desktops, laptops, and servers for suspicious activity. EDR is device-level threat identification and is able to automatically contain and remediate threats.
2. Network Detection and Response (NDR):
Scans network traffic to identify abnormal traffic, lateral movement, or indications of compromise. NDR assists in revealing the threats that bypass the endpoint protection and can warn the security teams about the possible breach.
3. Long Detection and Response (XDR):
Brings together several security layers, endpoints, network, cloud, and email into a single platform. XDR offers the ability to have holistic visibility, which allows quicker detection and coordinated response across all vectors.
4. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
Gathers and processes the data on security events across various sources and determines trends, abnormalities or signs of compromise. SIEM is typically employed together with MDR to deliver contextual and incident management notifications.
5. Cloud Detection and Response (CDR):
CDR targets the cloud environment, where they monitor suspicious workloads, applications and services. It provides security to cloud infrastructure that supplements endpoint and network surveillance.
Having knowledge of the various detection and response solutions, organizations can choose the appropriate combination to create an endpoint, network, and cloud environment-wide MDR strategy that is not only effective but efficient.
How MDR Works
The MDR Security works by combining human skills alongside advanced technology in detecting, investigating and dealing with threats in the cyber space of an organization. MDR does not passively send notifications to the user as traditional security tools do, but actively pursues threats and removes them.
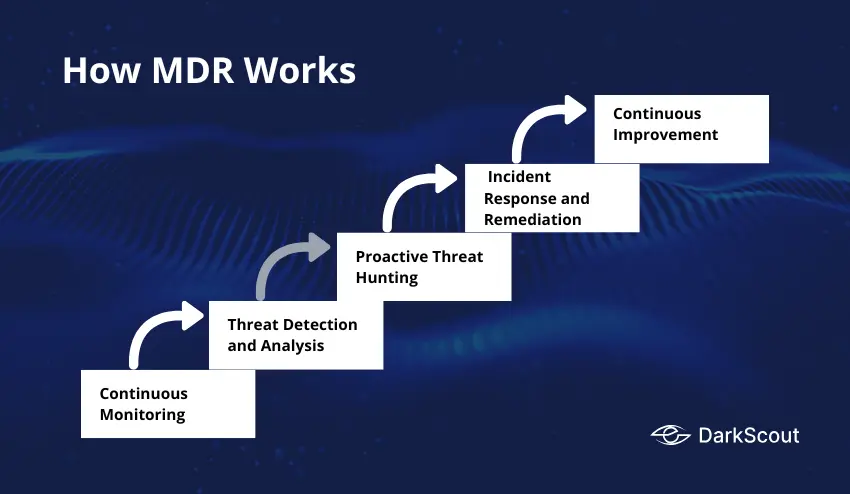
Step 1: Continuous Monitoring
MDR provides 24/7 Endpoint, Network, and Cloud System Threat Monitoring. Security tools and analysts are constantly monitoring suspicious activity, anomalies, or compromise indicators. This surveillance will enable the detection of any threats early enough.
Step 2: Threat Detection and Analysis
MDR identifies potential attacks and their magnitude with the assistance of advanced analytics, machine learning, and threat intelligence. It can be integrated with other tools like SIEM or XDR so that the alerts are contextualized to reduce false positives and maximize the effectiveness of responding.
Step 3: Proactive Threat Hunting
MDR teams actively investigate the latent threats, including Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), ransomware, or insider attacks. Threat hunting is preventative and eradicates threats to the operations before it can impact the organization, which enhances the overall security position of the organization.
Step 4: Incident Response and Remediation
After the confirmation of the threat, MDR initiates automated or manual response operations. This can be in the form of isolating infected endpoints, blocking malicious IP addresses or destroying malware. The security analysts also provide detailed full remediation guidance.
Step 5: Continuous Improvement
After the incidents are resolved, MDR teams learn about the attack and improve the detection rules and response in the future. This loop of feedback will make sure that the MDR system is created as new threats are introduced.
MDR provides an integrated, reactive security that cannot be compared to traditional security measures in terms of technology, threat intelligence, and human capacity.
Implementing MDR Security – Step by Step
MDR Security implementation needs an organized process to cover all areas and provide maximum security.
Step 1: Assess Security Needs
Before choosing a solution, organizations must identify critical assets, endpoints and possible threats. This includes the awareness of sensitive data, network vulnerability and systems which are of significance to the business.
Second, in-house versus outsourced requirements. Identify the security functions that can be handled in-house, and those that require MDR skills. This is to ensure that there is a clear scope of the MDR deployment.
Step 2: Select the Right MDR Provider
EDR, SOC coverage, and automated threat response are some of the key characteristics that can be considered when choosing a provider.
Make sure it can be connected to SIEM, cloud services, and any other legacy systems to ensure smooth monitoring.
Finally, take into account the pricing models and scalability. The answer should be applicable to your current requirements and grow with your company.
Step 3: Deploy and Integrate MDR Tools
Deploy MDR tools to your current security infrastructure and secure the endpoints, network, and cloud assets.
Monitoring of the institute, alert, and incident management procedures to enable your staff and the MDR provider to respond to threats.
Step 4: Establish Threat Hunting Practices
Develop proactive threat detection and investigations.
You will find anomalies and quiet threats using analytics and AI. Threat hunting needs to be done consistently to identify even the most advanced attacks like Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) on time.
Step 5: Monitor, Respond, and Improve
The 24/7 monitoring with your MDR provider and SOC.
Respond to incidents. Act upon your automated or manual remediation action plans.
Assess your performance regularly and improve your detection and response operations. Regularly improve your security posture overall.
This model of steps will help organizations implement MDR in a strategic manner, get maximum protection, stay in a proactive security posture.
Overcoming Common MDR Challenges
Although MDR Security is a good security solution, it can be difficult to implement and use by organizations. Such issues will be aware, and the implementation will be effective and successful in the long-term.
Integration with Legacy Systems: In some cases, modern MDR systems are difficult to integrate with legacy systems. Ready compatibility testing and incremental integration to prevent coverage lapses.
Fatigue of Alerts: Due to the constant monitoring, alerts are created in large numbers, and they may become overwhelming to teams. Combine contextual alerts and SIEM to give priority to the threats that matter and reduce noise.
Compliance: The MDR practices in organizations should be in line with the requirements of the region and the industry. Select suppliers to support audit and regulatory reporting.
Balancing Automation and Human Expertise: Threats that are complex require human analysis, and Automation is faster to respond to. Ensure that the combination of automated processes and human intervention is used to provide the most effective defense.
By working through these issues ahead of time, organizations can be confident that their MDR Security is performing as well as it can and are in a high cybersecurity posture.
MDR Security for SMBs – Tailored Approach
The use of IT is also limited, which means that SMBs will be the most vulnerable to cyber threats. MDR Security is a scalable, low-cost solution that can provide the protection of an enterprise without the need to recruit a dedicated security team.
When it comes to SMBs, prioritization should be placed on critical assets and high-risk endpoints and networks. Providers customize MDR services to the size, budget, and risk profile of the organization.
In addition, MDR solutions that target SMBs are more likely to have easy-to-use dashboards, automatic notifications, and simplified reporting, allowing smaller teams to manage threats more easily. To stay ahead of cyber attacks and secure business continuity, SMBs can be proactive in both hunting threats and monitoring them 24/7.
MDR helps SMBs to protect sensitive information, resolve compliance requirements, and enhance their overall cybersecurity without overloading internal resources.
Conclusion
MDR Security offers a dynamic, multifaceted protection against current cyber threats to organizations. Using a combination of sophisticated technology, threat intelligence, and human resources, MDR detects, investigates, and responds to attacks with greater speed than conventional security solutions.
Strategic implementation of MDR, including the assessment of security requirements, choosing the appropriate provider, installing the tools, and ongoing monitoring, will help any organization, big and small, to secure its critical assets and ensure business continuity.
In the case of SMBs, MDR can provide the protection of an enterprise-level with complexity and expense of a full in-house security team. In larger organizations, it improves infrastructure that is already in place and shortens dwell time on complex attacks, such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
With the evolving cyber threats, MDR allows organizations to be ahead of the attackers and ensure compliance and improve their cybersecurity posture. Nowadays, investing in MDR Security is not a choice anymore, but one of the major steps toward resilient, state-of-the-art cybersecurity.