The timeless problem of modern cybersecurity teams is the excessive number of alerts and insufficient time. False positives are common, and sorting them out, as well as redundant work, is a waste of time by SOC analysts, slowing down the investigation and posing life-threatening delays.
That is why SOAR security is becoming a necessity. SOAR is an acronym that means Security Orchestration, automation and response, and it assists teams to integrate their security tools into a single workflow and automate common activities such as triage, enrichment, and ticketing.
Incident response is quicker and more regular with SOAR. Playbooks can enable teams to contain threats as fast as possible and minimize human error instead of responding to each alert manually. In this guide, we are going to describe what SOAR is, how it functions, and how it can enhance your cyber defense.
What Is SOAR Security?
SOAR Security is an abbreviation of Security Orchestration, Automation and Response. It is a model that is aimed at assisting cybersecurity teams in managing alerts, coordinating workflows, and responding to threats more quickly and efficiently.
- Orchestration: Relates various security tools and systems to a workflow. It makes sure that alerts, logs and events of various sources are not isolated but rather integrated.
- Automation: Substitutes manual processes, including the creation of tickets, triage of alerts, or enriching threats, with automated processes. This minimizes human error and liberates the analysts to do the higher level work.
- Response: Allows the coordinated response to threats within a timely manner. It can be blocking an evil IP, isolating an infected computer, or informing interested parties, but SOAR will make sure that the response is organized and standardized.
Consider SOAR as the cybersecurity air traffic control. Rather than analysts tracking each alert manually, SOAR coordinates tools, automates repetitive tasks, and makes sure that threats are dealt with before they grow out of control.
You May Also Like: What Is a Secure Web Gateway? Features, Benefits, Types, and Future Trends
The Importance of SOAR Security
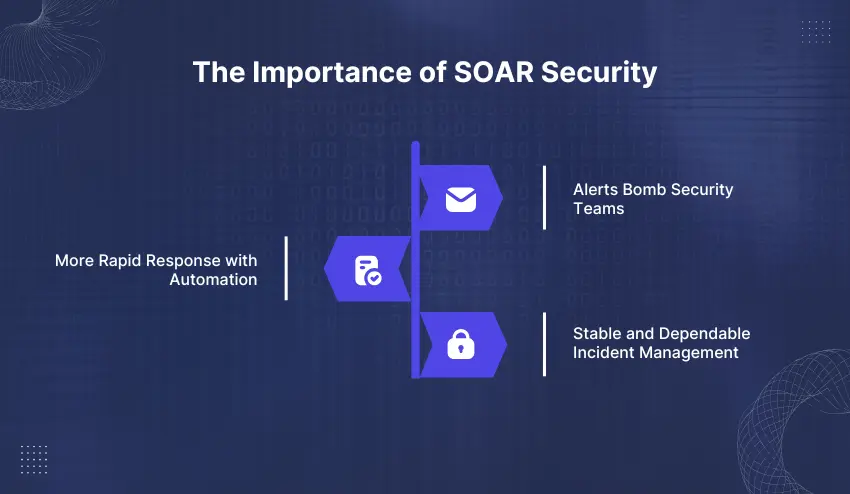
Alerts Bomb Security Teams
The contemporary SOCs have to deal with a daily deluge of alerts. Manual processes are unable to keep pace and analysts usually spend time on false positives and repetitive processes. This delays the response and exposes the possibility of missing actual threats.
More Rapid Response with Automation.
SOAR security can alleviate this pressure by automating the mundane processes and grouping security tools into a single process. It assists the teams in prioritizing the high-risk incidents and responding quicker, enhancing detection and containment.
Stable and Dependable Incident Management
SOAR provides automated playbooks, which means that incidents are managed in a consistent manner. This will minimize human error, enhances accountability and helps with compliance.
Why SOAR Matters Today
SOAR transforms chaos in alerts to orderly response processes. It is no longer an option but a necessity to keep up with the current day cyber threats.
How SOAR Security Works
SOAR security is created by integrating orchestration, automation, and response into a smooth workflow that lessens the workload on security teams and enhances efficiency. The following is a step by step analysis of a typical SOAR process:
1. Alert Intake
All the incoming alerts of SIEM, firewalls, endpoints or threat intelligence feeds are centralized. Such centralization will make sure that no alert is overlooked and will allow viewing security events in one place.
2. Enrichment
Each alert receives enrichment. For example, the recorded IP addresses are searched in threat intelligence bots, user accounts are reviewed, and the system logs are reviewed. This gives the analyst the full context before taking action.
3. Decision & Triage
Alerts are categorized based on preset rules and playbooks depending on the severity. Low priority alerts may be automatically processed and the high-priority threats are escalated to analysts.
4. Automated Response
SOAR activates automation of actionable alerts. Examples are blocking malicious IPs, quarantining infected devices or informing the concerned stakeholders.
5. Documentation & Reporting
All steps are automatically logged to audit, comply and improve. This will keep the teams accountable and enable them to perfect playbooks with time.
Sample Playbook: A phishing email notification activates automatic analysis of URLs and attachments, isolates impacted endpoints, alerts the SOC team, and creates a report- all automatically.
Through coordination of these actions, SOAR security decreases the response time, minimizes human error and enhances the efficiency of the SOC in general.
SOAR Security vs SIEM (and Other Tools)
SOAR security is often mistaken to SIEM by many organizations, yet they are not similar. The difference is important to maximize your security operations.
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): It is mainly concerned with gathering, storing and analysing logs of various systems. It creates alerts when unusual activity is identified, yet it does not automatically react or organize working processes.
SOAR Security: Does not stop at alert generation. It coordinates various security tools, automation of repetitive processes, and offers an organized reaction to incidents. SOAR makes sure that threats are dealt with in real time.
How They Work Together:
- SIEM determines and ranks threats.
- SOAR accepts those alerts and runs automated playbooks to investigate them, contain them, or remediate them.
Quick Comparison Table:
| Feature | SIEM | SOAR Security |
| Purpose | Detect threats | Automate and respond |
| Alert Handling | Manual or semi-automated | Fully automated playbooks |
| Integration | Moderate | High (connects multiple tools) |
| Response Capability | Minimal | Extensive |
Integrating SIEM and SOAR can provide organizations with visibility and actionable efficiency to make security operations quicker, smarter, and reliable.
Use Cases Of SOAR
SOAR security is not a mere concept- it has been put into practice in various fields of cybersecurity. The most typical use cases are as follows:
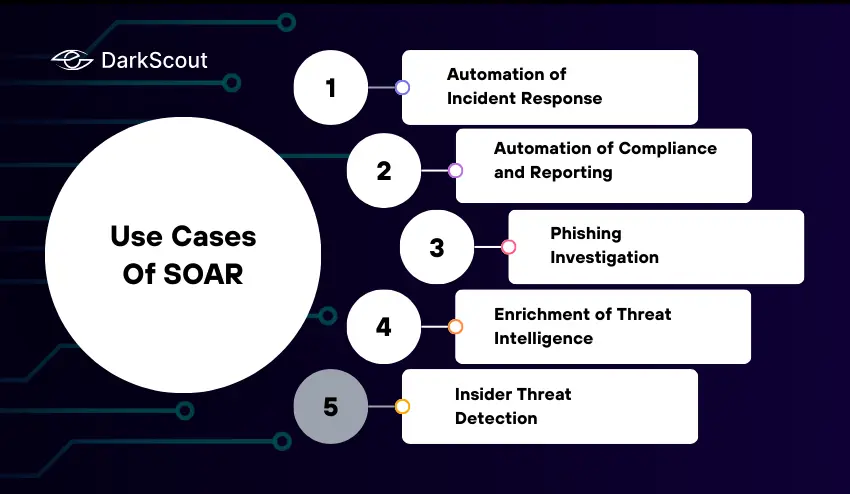
1. Automation of Incident Response.
SOAR automates the process of repetitive tasks in incident response, including checking alerts, creating tickets, and initial containment. This saves the time of responding and enables analysts to concentrate on vital decision-making.
2. Phishing Investigation
Suspected phishing emails can automatically analyze alerts. SOAR is capable of checking links, scanning attachments, isolating affected devices, and notifying users, without manually doing so.
3. Enrichment of Threat Intelligence.
SOAR extracts the information in threat intelligence feeds and compares threat alerts with established malicious indicators. This gives the SOC teams contextual information to focus on actions.
4. Automation of Compliance and Reporting.
Security teams are able to produce reports automatically, follow audit trails, and guarantee regulation compliance such as GDPR or HIPAA, which lowers the amount of manual documentation.
5. Insider Threat Detection
SOAR is able to track abnormal user behavior, automatically alert suspicious activity, and initiate pre-approved response actions to avert possible insider threats.
These applications show that SOAR security enhances efficiency, minimizes human error and enhances the overall protection. The response times and threat containment have been improved in organizations that apply SOAR.
SOAR Platforms Evaluation
The selection of the appropriate SOAR security platform is essential to the fullest effect. The following are the main aspects to take into consideration:
- Connectivity to Existing Tools.
Make sure that the platform integrates with your SIEM, endpoint detection systems, firewalls, threat intelligence feeds and ticketing. The more integrations, the more your workflows are efficient.
- Playbook Management
Find solutions that enable automated playbooks to be created, customized, and managed easily. A scalable playbook framework will make sure that your SOAR is adjusted to changing threats.
- Scalability and Cloud Readiness.
Your SOAR solution must be able to cope with growing volumes of alerts and grow with your organization. Cloud-enabled systems can be flexible and have a reduced maintenance overhead.
- User Interface and Experience (UI/UX)
An easy to use, intuitive dashboard makes it easy to learn the alerts, workflows and system status. Even with the presence of automation, poor UI can delay response times.
- Community and Vendor Support.
It is easier to troubleshoot, optimize playbooks, and learn best practices with strong customer support, documentation, and an active user community.
- Return on Investment (ROI)
Think about the effect on response time, workload on analysts, and the security posture. Consideration of whether the platform will save time, reduce breaches, and justify costs.
When such factors are carefully evaluated, organizations will be able to choose a SOAR platform that will not only be suitable to their present needs but also enable them to grow in the long run and manage the threats.
Best Practices to Implement SOAR Security
To have the SOAR security implemented successfully, you need to plan and coordinate it with the workflow of your team. The following are best practices that have been proven:
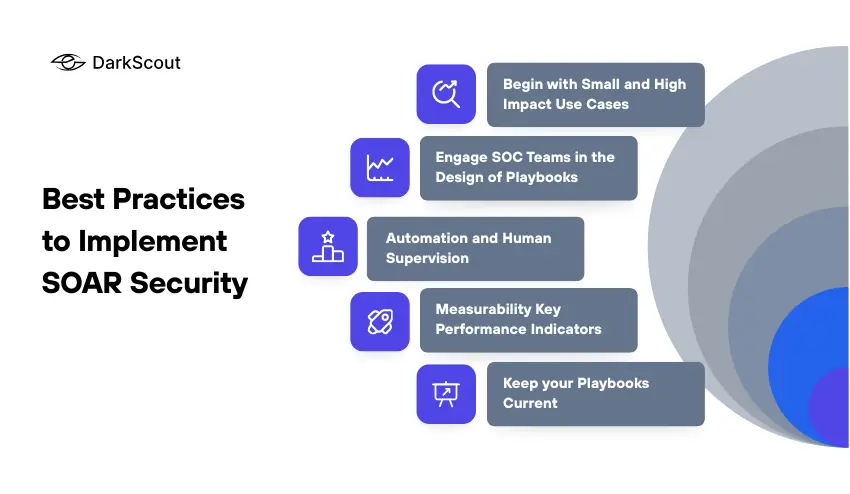
1. Begin with Small and High Impact Use Cases.
Start with some of the most important processes, such as phishing response or malware triage. This assists in proving the quick wins and gives confidence in automation prior to scaling.
2. Engage SOC Teams in the Design of Playbooks.
The specialists in day-to-day operations are analysts. Work together with them to create playbooks that are based on the real-life workflow and minimize the extraneous steps.
3. Automation and Human Supervision.
Automation of alerts should not be applied to all of them. Find the tasks that can safely be automated and the complex decision-making to human beings. This keeps quality and responsibility.
4. Measurability Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Track KPIs such as Mean Time to Respond (MTTR), automated processes, and analyst productivity. These KPIs are the value added of SOAR, and keep you going on in a cyclic way.
5. Keep your Playbooks Current
Threats are dynamic and SOAR processes depend on it. Review and revise playbooks on a regular basis using new intelligence and incident reviews, and lessons learned.
These best practices would enable organizations to achieve the best benefits of SOAR security, reduce the operational risk, and establish a more efficient SOC.
Conclusion
SOAR security is not optional anymore, but a requirement to organizations that want to enhance their cybersecurity defenses. SOAR converts unstructured alert streams into workflows by orchestrating tools, automating repetitive processes, and responding more quickly.
Knowledge of SOAR enables organizations to save time in responding, reduce the number of human errors, and enhance the overall efficiency of the SOC. SOAR offers a reliable, scalable, and structured solution whether it is phishing attacks, malware alerts, or compliance reporting.
Organizations can also be able to maximize the value of SOAR security by applying best practices, selecting the appropriate platform, and continually refining playbooks, so that their teams are able to work smarter rather than harder and stay ahead of the changing threats.