Cyber threats are no longer an issue only of big technology companies; it is an issue of every business, government, and nonprofit. Hackers target operating systems, cloud-based systems, and even IoT to steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, or demand money. Cases of cyber security in the past few years have included ransomware locking down hospitals, phishing attacks draining bank accounts, and supply chain attacks hacking trusted software vendors.
The upside? Modern methods of cybersecurity and tools enable detecting and stopping such attacks before they are able to cause any damage. This guide will explain what cybersecurity is, why it is needed, what the most common cyber threats are, some real-life examples of cyber security, the current trends in technology, and the best practices that you can apply today.
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber security involves the process of guarding networks, systems, and information against assaults and unlawful access. It is a combination of technology, procedures, and prepared individuals to prevent the onset of damage by threats.
Talking about cyber security examples, we do not mean only antivirus software or firewalls. It is comprised of endpoint security, access controls, threat intelligence, and detection systems that avert a breach prior to its propagation.
Effective cyber security prevents leaks of sensitive information, assists businesses in their daily activity, and enables the fulfillment of compliance regulations.
Why Cyber Security is Needed
All businesses, government, and nonprofits are exposed to cyber risks. Now, attackers are attacking both small and big organizations by seeking vulnerabilities in operating systems, cloud systems, and logins to access data or cause interruption of services. There is no safe industry, and even minor weak points will be sufficient to cause infiltration of a malicious force that is focused on that target.
Examining recent cyber security examples, the ransomware attacks have caused hospitals to shut operations, phishing attacks have made employees give away bank login details, and supply chain attacks have distributed malware via trusted suppliers. The result of these cases is data loss, reputation damage, and serious penalties, most likely in the form of legal charges or huge fines. In the absence of robust security, the process of recovery takes a very long time (at times irrecoverable).
Common Cyber Threats
Here are some of the most common attacks you’ll see in cyber security examples today:
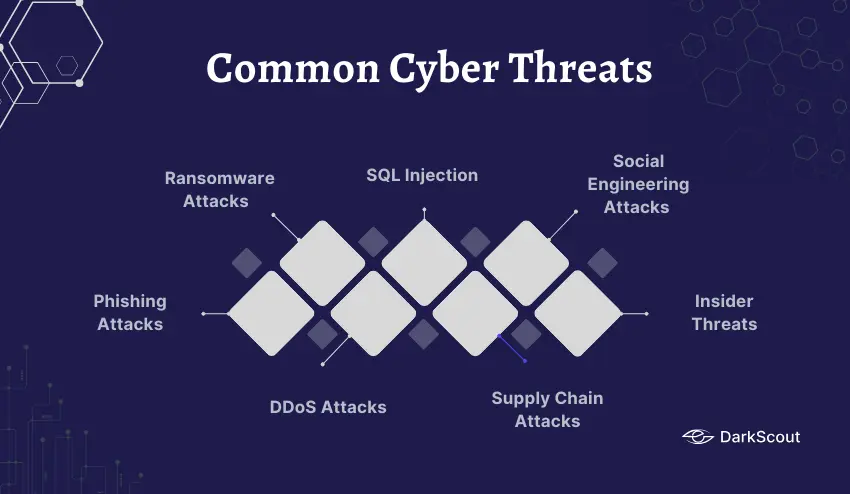
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is one of the most common threats, consisting of false emails, text messages, or websites that are aimed at deceiving individuals into providing their logins, bank account information, or other sensitive information. Scammers usually pose as banks, payment services, or internal company contacts and use urgent words to cause panic and make people act in a hurry.
2. Ransomware Attacks
Malicious software encrypts the files of an organization, and the organization is required to pay to get the decryption key. The victims can experience days or weeks of downtime, loss of important business data, or even have files stolen and posted online. Even when the ransom is paid, there is no assurance that the attacker will provide full access back.
3. DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service is an attack that overwhelms a targeted server, website, or network with massive traffic until it crawls to a halt or crashes. This may deny genuine users access to services, causing loss of revenue and tarnishing the reputation.
4. SQL Injection
In SQL injection, hackers can use weakly secured databases to inject malicious SQL code into any input field, like a search box or a login box. This enables them to access, alter or delete sensitive records, in some cases gaining full control of the database.
5. Supply Chain Attacks
Attackers hack an organization that is trusted by a vendor, software supplier, or service provider to target several organizations simultaneously. Since the threat is a legitimate source, it can evade most of the normal security measures and go undetected for months.
6. Social Engineering Attacks
Attackers do not hack into systems; they exploit human behavior. They may pretend to be IT staff, create some fake emergency, or gain confidence over time to convince people to violate security policies or reveal sensitive information.
7. Insider Threats
Employees, contractors, or business partners who have legitimate access to the system can either maliciously or accidentally do harm. This may be stealing intellectual property, leaking sensitive files, or failing to follow security policies, and this opens the door to external attackers.
Only knowing these threats isn’t enough; you have to be prepared. In the following cyber security examples, we’ll explore how different defenses, tools, and best practices can help reduce these risks and protect sensitive data from ever-evolving cyber attacks.
Cyber Security Examples in Real Life
Cyber security examples in the real world demonstrate that various industries customize their protections to the threats they face. Examining the implementation of these strategies will allow you to determine which strategies might help to improve your security position.
1. Law Firm Endpoint Security
Legal firms deal with highly confidential information of clients and are therefore a prime target of attackers. One medium-sized company implemented endpoint security on all laptops and mobile devices of employees. The tools were used to scan the malicious code, track abnormal file activity, and prevent suspicious downloads. In the case where a phishing email tries to execute ransomware, the endpoint system automatically isolates the infected machine, preventing the spread to sensitive legal documents.
2. Zero Trust Banking
Financial institutions are under continuous attack on accounts, transaction systems, and internal databases. One regional bank adopted Zero Trust architecture, that is, no user or device was trusted by default. All logins, transactions, and account data requests were multi-factor authenticated and verified on an ongoing basis. Despite legitimate credentials, the network security team of the bank was alerted to review the unusual network activity.
3. AI Security in Healthcare
Hospitals need quick access to the information of the patients without violating their privacy. One healthcare provider has used AI security to monitor application security and database logs in a real-time manner. When AI detected an off-hours pattern of logins to patient records, the incident response team found a compromised staff account and locked it down before records were stolen. This also ensured the confidentiality of the medical data laws.
4. Cloud Security for E-Commerce
Online retailers have to be very concerned about cloud security because they handle large volumes of payment transactions. A growing e-commerce organization encrypted payment information, restricted access controls, and placed intrusion detection on its cloud platform. The system blocked the request when an overseas IP tried to make unauthorized access and informed the security teams before any breach of payment card data could occur.
5. IT/OT Security in Manufacturing
Modern factories have IT systems and operational technology (OT) integrated to manage production lines. One manufacturer segregated its OT network to the corporate IT systems and incorporated IT/OT security surveillance. In the case of malware being introduced through a compromised supplier system, the segmentation and network security rules ensured that it could not cause any issues to production equipment.
6. Email Security for Public Agencies
Phishing attacks are common in government agencies via email. An email security filter with advanced threat detection was implemented by a city administration. Attachments and links that were suspicious were quarantined, and the chances of social engineering attacks that would lead to a breach of citizen data were minimized.
7. IoT Security in Smart Buildings
As the number of devices linked to the internet increases, Internet of Things (IoT) security is becoming a necessity. The device authentication and encrypted communications were installed in a smart office building with IoT-enabled HVAC and lighting systems. This ensured that hackers did not get access to the network of the building via unsecured IoT devices.
One thing is clear with these cyber security examples: endpoint security, Zero Trust, cloud security, and IoT security all need a layered approach to protection in the modern environment. All the defense strategies deal with certain threats, yet altogether they create a powerful security posture that can protect any industry.
Tech Trends Driving Cyber Security
Cyber threats are evolving fast, and cyber security examples from today look different from those a decade ago. Key trends include:
- AI Security- Machine learning identifies abnormal behavior in real time and enables security teams to respond immediately.
- Generative AI Risks- AI is used by criminals to create convincing phishing messages and fraudulent websites that circumvent conventional filters.
- Cloud Adoption- With the migration of data to the cloud, the security of these environments has become of utmost importance.
- IoT Security- Devices such as cameras and sensors that are connected should be secured to prevent them from being used as attack entry points.
- Zero Trust- No user or device is trusted; all actions are verified.
- Threat Intelligence- Real-time intelligence assists in preventing damage by blocking threats.
These trends highlight the need for constant adaptation in cyber security strategies.
Top Cybersecurity Platforms
Selecting a proper cybersecurity platform is among the most significant actions to create an effective security posture. These are some of the best solutions that organizations use in order to defend against cyber threats:
DarkScout
DarkScout is an effective threat intelligence and exposure management solution that helps identify risks prior to them becoming breaches. It constantly checks the data leaks, compromised credentials, and attack surface vulnerabilities. DarkScout provides security teams with practical intelligence to prevent threats before they occur, which is why it is a leading solution to proactive cyber defense.
Features:
- Custom Investigations – Custom threat intelligence based on darknet and deep web sources.
- Darknet Threat Assessment – Find exposed credentials, ransomware mentions, and vulnerabilities.
- Threat Actor Analysis – Profile the cybercriminal groups and their attack techniques.
- Darknet Monitoring – Constant monitoring of dark forums and dark markets with real-time notifications.
- Brand Protection – Identify fake products, unlicensed use of brand, or breach of references.
- Data Acquisition – Retrieve exposed credentials or sensitive data in a safe manner.
- Vision UI & APIs Unified dashboard and integration tools (Search, DarkSonar, Datafeeds).
Darktrace
A cybersecurity platform powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning that identifies and eliminates threats in real time across cloud, network, and endpoint.
CrowdStrike Falcon
An endpoint protection platform that integrates next-gen antivirus, EDR, and rich threat intelligence to prevent breaches in real-time.
Palo Alto Networks
Provides high-end network and cloud security with in-built Zero Trust frameworks to protect users, applications, and data against contemporary threats.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Offers enterprise-level endpoint security, vulnerability management, and automated response to minimize the impact of the attack.
When integrating a proactive tool such as DarkScout with other security solutions, organizations can address more attack vectors and minimize the likelihood of expensive incidents.
Best Practices to Protect Sensitive Data and Prevent Unauthorized Access

The following are practical measures supported by cyber security examples:
- Implement Access Controls – Give employees just the required access.
- Activate Multi-Factor Authentication- Authenticate log-in credentials using secondary authentication.
- Maintain Systems Current- Update operating systems and applications.
- Run Security Awareness Training – Train the employees to identify phishing emails and social engineering.
- Conduct Penetration Tests – Find out what is weak about you before the attackers.
- Encrypt Data – Protect all data that are stored and sent.
- Use Endpoint Security – Block malware and unauthorized access attempts.
- Monitor Continuously – Identify and act upon threats when they are still in their initial phases.
When combined, these measures greatly improve your security posture.
The Cyber Security Skills Gap
Many cyber security examples show that tools aren’t the only things you need; you also need skilled people. The industry is experiencing a lack of skilled personnel capable of responding to incidents, tracking the attack surface, and implementing high-end security solutions.
Closing this skills gap involves training, automation where it is possible, and outsourcing to third-party specialists where necessary.
Conclusion
By learning from best practices, applications, and real-life examples in cyber security, organizations will be able to know how to safeguard sensitive information and avoid unauthorized access. It is all about proactive monitoring, employee awareness, and the proper security platforms such as DarkScout.
Cyber threats are here to stay- however, by taking the appropriate measures you can be one step ahead and protect your operations.